CRM - AI Voice Assistant
From typing to talking: logging activities the moment they happen.
Produced video by ForceManager for Android devices. More info ForceManager
You know the moment: a rep steps out of a meeting, glances at the clock, and heads to the car. They should log the visit and set a follow-up, but the old calendar flow means opening a form, hunting fields, typing on a small keyboard, and wrestling with validations. Most entries get postponed to “tonight”… and many never happen. Over time that gap erodes forecast quality and weakens follow-ups.
This project set a simple goal that’s hard to execute: make logging an activity as natural as saying it out loud.
What changed when reps stopped typing and started talking
In just two weeks, switching from typing to talking cut task time by 54%, reduced taps by 68%, and boosted activity completion by 24 points — transforming routine admin work into something as natural as conversation.
Tasks now take under one minute -and reps finally log them on time.
The proposition: voice first, confirm to save
My role was to translate those pain points into clear design decisions, iterate with the team, and validate with users until we reached a trustworthy and scalable experience.
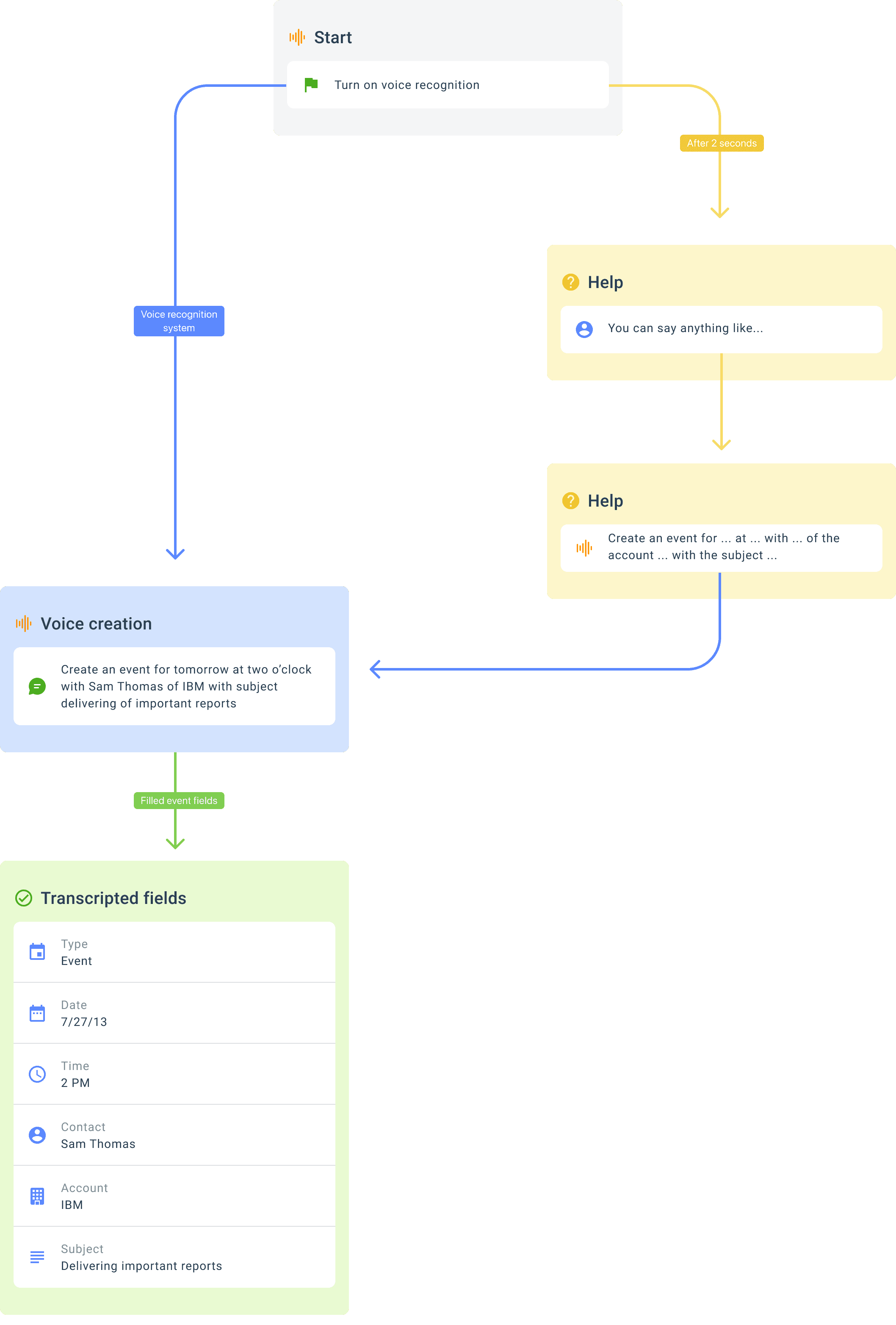
I added a home-screen shortcut with voice first and a confirmation card. Saying
“Create a meeting for next week with Victor from IBM, with the title: Presentation of campaigns.
In a two-week pilot with 36 reps (ES/EN):
Side effects: +18 pp next-day data completeness and −23% tickets related to save/validation errors.
A 40-rep team recovers ~14.6 hours/week for selling.
Designing the conversation
The craft lives in the choreography between what people say, what the system understands, and what we confirm.
I defined scripts with real utterances and microcopy that builds trust —
“Saving a Visit for Ana Sosa tomorrow at 10:00 at Barcelona HQ. OK?” —
and repair prompts that keep the flow moving.
I also built small but important behaviors: auto-pause on incoming calls, clear mic states, and tactile confirmation so the assistant feels reliable even when you’re on the move.
Research & validation
I interviewed reps and observed in-context use — leaving visits, in cars, in hallways — to understand how they interacted with the CRM in real conditions.
I ran moderated testing with prototypes and collected usage diaries during the pilot.
A key finding emerged: a strong sense of control drives trust.
That insight led to two critical patterns — a pre-save summary and an edit view for the transcript — giving users visibility before committing, and reducing anxiety around voice recognition errors.
MILESTONE 3 - DATA & INSIGHTS
What people taught us
In testing, users naturally simplified their phrasing into a consistent structure: [type] + [date] + [time] + [who] + [topic]. That pattern informed our grammar and reduced retries. Two real-world constraints mattered most: ambient noise and duplicate names. We handled them with confidence thresholds that trigger clarifying questions and a disambiguation step that favors recent contacts and current location.

MILESTONE 4
Scenarios and error handling
I designed for the expected, the likely, and the messy — because real life rarely fits a script.
Each scenario revealed how the assistant needed to behave to stay helpful, not clever.
Expected -the easy ones
"Tomorrow at 9" or "this afternoon"
Straightforward commands with clear intent and time context.
Clear commands, instant save.
Likely -the real life twists
“Call Victor tomorrow.”
The assistant temporarily stores context until it identifies the right contact or account, then completes the action.
Missing info, temporary context, smart follow-up.
Edge cases -the messy reality
"…meeting with Lora at mine..."
Voice input isn’t perfect. Users sometimes restart dictation when unsure what’s captured.
Interrupted input, editable transcript for control.
Validation that moved the needle
Together with iOS engineering we ran a two-week A/B pilot with 36 reps (ES/EN). We measured the same KPIs on both experiences—time to create, taps to complete, completion rate of started tasks, repair events, and post-task satisfaction.
Key Decisions
Voice first, confirm to save: one confirmation card with editable chips instead of a multi-step form.
Progressive disambiguation: ask only when something is missing (“which Ana?”).
Graceful degradation: every voice step has a touch alternative.
Trust microcopy + haptics/earcons for immediate feedback.
Explicit privacy: clear mic permission; no raw-audio storage.
Calendar default page

Help script (after 2s.)

Reading data

Transcription edition
What changed in the field
The most valuable shift was a habit: reps closed the admin loop at the door, not at night. Managers saw cleaner next-day data for forecasts and follow-ups, while support tickets about “can’t save” validation errors dropped.
Produced video by ForceManager for Android devices. More info ForceManager
Reflection & learning
What worked: anchoring the experience to the moment of capture; confirm-before-save; comparable telemetry for fair A/Bs.
What didn’t: generic vocabularies; we got better results with domain-tuned grammars.
Next: per-user language preferences, richer earcons for noisy contexts, admin-visible telemetry, and expanded intents (dictated notes, suggested follow-ups, email drafts).
